[ad_1]
The massive image: If there’s one factor that generative AI is meant to be good at, it is analyzing the written phrase. Nonetheless, two research recommend that this capability might have been overhyped. One examine demonstrates that Gen AI struggles with understanding long-form books, whereas one other exhibits that these fashions discover answering questions on movies difficult. That is one thing corporations ought to think about as they increase their workforce with Gen AI.
Generative AI has struck concern within the hearts of creators of all sorts, however significantly for individuals who take care of the written phrase. Freelance work for copywriters has been drying up, largely due to the variety of GenAI engines which have sprung up in current months. Different types of gig work have been affected too, regardless of the rising realization that AI is not solely dwelling as much as its authentic hype.
Two new research present a number of the limitations of those chatbots, revealing they might be extra in depth than beforehand realized. Each research study how effectively GenAI could make sense of huge quantities of knowledge. Particularly, one examined the power of AI language fashions to know and proceed lengthy tales, evaluating how effectively these fashions can comprehend and construct upon prolonged narratives past typical short-range processing.
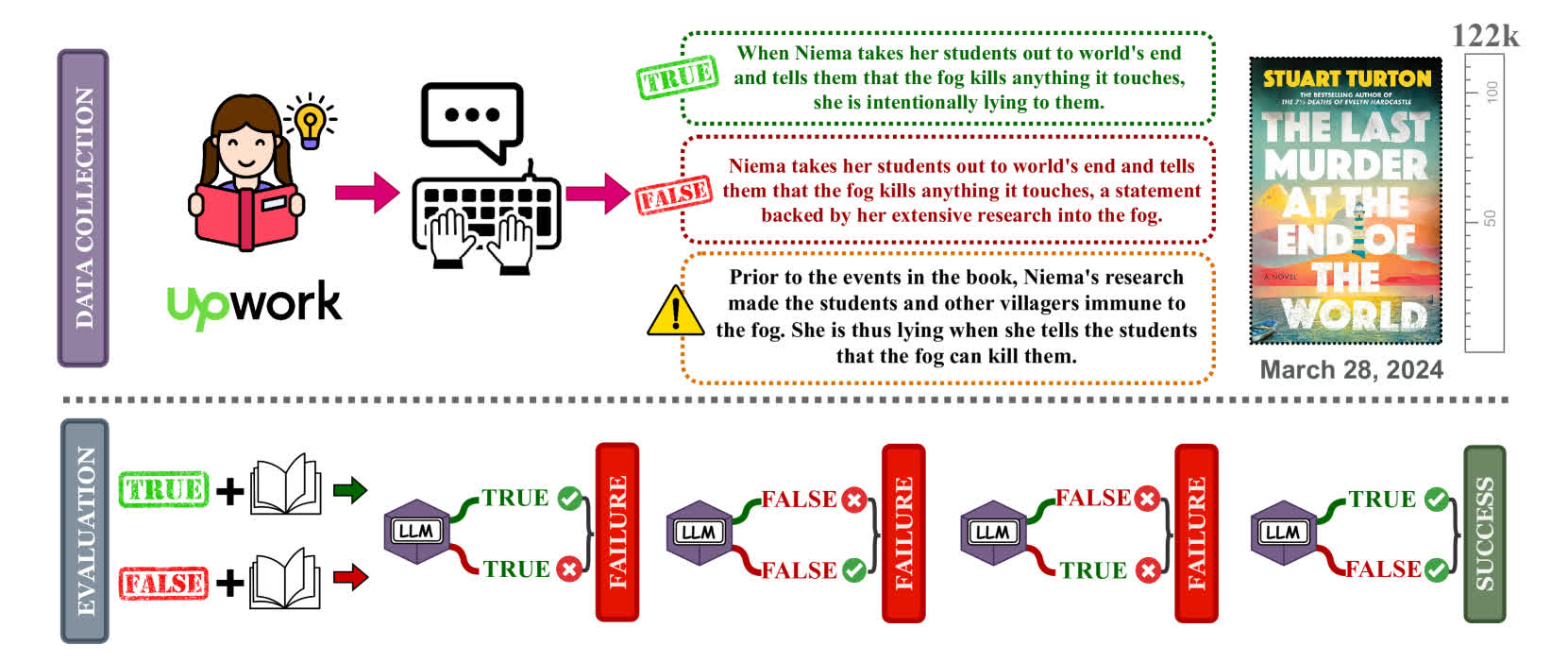
For one e book of 520 pages, the researchers discovered that Gemini 1.5 Professional answered the true/false statements accurately 46.7% of the time, whereas Gemini Flash answered accurately solely 20% of the time.
The opposite examine centered on evaluating the efficiency of imaginative and prescient language fashions. Each research discovered that AI falls brief, together with Google’s newest Gemini generative AI fashions, which emphasize their capability to course of and analyze massive quantities of knowledge as their promoting factors.
For instance, Gemini 1.5 Flash can analyze one hour of video, 11 hours of audio, or greater than 700,000 phrases in a single question, in response to Google. In a presentation to journalists, Google confirmed the way it may analyze a 14-minute video in a single minute. However its grasp of the context – not less than the long-form written context – is suspect, in accordance to Marzena Karpinska, a postdoc at UMass Amherst and a co-author on one of many research. “Whereas fashions like Gemini 1.5 Professional can technically course of lengthy contexts, we’ve got seen many circumstances indicating that the fashions do not really ‘perceive’ the content material.”
Karpinska, together with researchers from the Allen Institute for AI and Princeton, requested the fashions to judge true/false statements about current fiction books, asking about particular particulars and plot factors.
For one e book round 260,000 phrases, or 520 pages, the researchers discovered that Gemini 1.5 Professional answered the true/false statements accurately 46.7% of the time whereas Gemini Flash answered accurately solely 20% of the time.
GPT-4 achieved the very best accuracy at 55.8% on the NoCha (Novel Problem) dataset. The examine additionally discovered that the model-generated explanations for his or her selections have been typically inaccurate, even for accurately labeled claims.
“We have observed that the fashions have extra problem verifying claims that require contemplating bigger parts of the e book, and even the complete e book, in comparison with claims that may be solved by retrieving sentence-level proof,” Karpinska stated. “Qualitatively, we additionally noticed that the fashions wrestle with verifying claims about implicit data that’s clear to a human reader however not explicitly acknowledged within the textual content.”

Within the second examine, researchers discovered that throughout varied duties, together with mathematical reasoning, visible query answering (VQA), and character recognition, a various set of VLMs wrestle because the visible context size will increase. Typically, present state-of-the-art VLMs have problem ignoring irrelevant data when answering queries in lengthy visible contexts.
The co-authors created a dataset of photos, equivalent to a photograph of a birthday cake, paired with questions for the mannequin to reply in regards to the objects depicted within the photos. They picked one of many photos at random and inserted “distractor” photos earlier than and after it to create slideshow-like footage.
“On actual question-answering duties over photos, it seems to be significantly exhausting for all of the fashions we examined,” Michael Saxon, a PhD scholar at UC Santa Barbara and one of many examine’s co-authors, stated. “That small quantity of reasoning – recognizing {that a} quantity is in a body and studying it – is perhaps what’s breaking the mannequin.”
Right here too, Gemini Flash did not carry out effectively when requested to transcribe six handwritten digits from a slideshow of 25 photos, getting round 50% of the transcriptions proper and 30% with eight digits.
[ad_2]