[ad_1]
Ahead-looking: Researchers from California and South Korea have found a means to make use of a water-soluble polymer as a brand new, recyclable materials for 3D printing. This polymer may also be mixed with different supplies, akin to carbon nanotubes, to boost its robustness. This innovation might result in extra sustainable elements for digital circuits and bio-delivery methods.
There are numerous strategies of 3D printing utilizing uncooked supplies like filaments and liquid polymers. Nevertheless, these processes typically require a number of steps and typically complicated instrumentation to create constructions. For instance, making a construction with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) requires melting and cooling the filament. Different strategies, like resin-based 3D printing, require ultraviolet gentle to remedy the liquid polymer.
The polymer often called PNIPAM (poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)) was first synthesized within the late Nineteen Fifties and is utilized in numerous purposes at present, together with biosensing, managed drug supply, and water purification. Researchers from the College of California, San Diego, and Hanyang College in South Korea found that PNIPAM can be utilized as a recyclable ink for 3D printers. This breakthrough comes sizzling off the heels of one other 3D printer innovation referred to as CHARM3D, developed by researchers in Singapore.
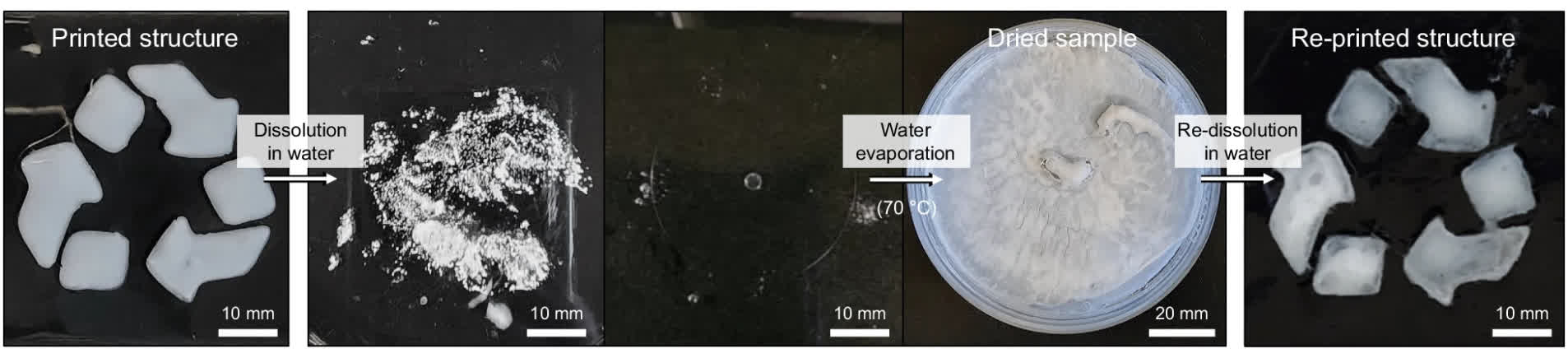
The researchers used a way referred to as the salt-out impact. Introducing PNIPAM to a calcium chloride salt answer varieties bodily crosslinks, which result in nearly instantaneous solidification with out the necessity for warmth, gentle, or poisonous solvents. The 3D-printed PNIPAM construction can then be dissolved in water and reclaimed for recycling and reuse.
There have been issues that PNIPAM’s water-soluble and temperature-sensitive properties would possibly restrict its purposes. Nevertheless, the excellent news is that PNIPAM may be mixed with different supplies to boost its thermal and mechanical properties.
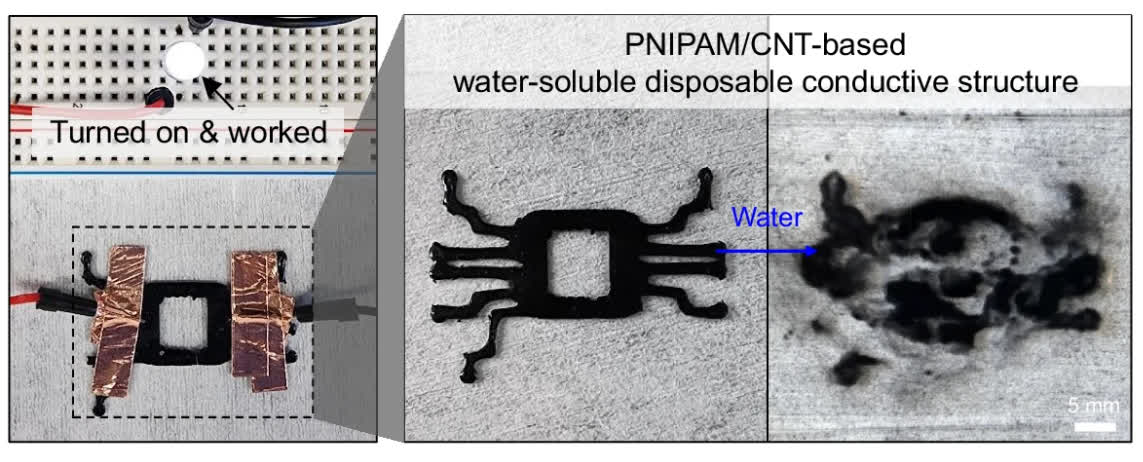
In a single instance, the researchers mixed PNIPAM with carbon nanotubes to create an electrically conductive circuit, which was used to energy an LED gentle. After the check, they dissolved the circuit and reclaimed the PNIPAM/CNT materials.
Additionally learn: Sustainable Computing, Defined
This demonstrates the potential of purposes utilizing water-soluble circuits, which might begin a brand new wave of recycling electronics and lowering e-waste.
Possibly within the not-so-distant future, know-how producers can flex their use of PNIPAM/CNT-based circuits of their sensible units.
[ad_2]