[ad_1]
One thing to sit up for: Night time imaginative and prescient goggles have their makes use of but in addition many drawbacks, together with their weight. A brand new improvement eliminates this cost-benefit evaluation – actually, it may revolutionize night time imaginative and prescient applied sciences as we all know them. Researchers have created an infrared filter that’s thinner than a chunk of cling wrap, weighs lower than a gram, and may be positioned over commonplace eyeglasses to permit the wearer to see in the dead of night.
Night time imaginative and prescient applied sciences have a variety of purposes, from sports activities to navy and medical operations. Nonetheless, they’re restricted by cumbersome light-processing and cryogenic cooling parts, in addition to their reliance on slender bandgap semiconductors, reminiscent of InGaAs, which require low-temperature operation and have excessive noise ranges.
Moreover, these techniques typically block seen gentle. This gear can weigh greater than two kilos, making it impractical and presumably unsafe to strap on a pair of goggles and go for a nighttime run.
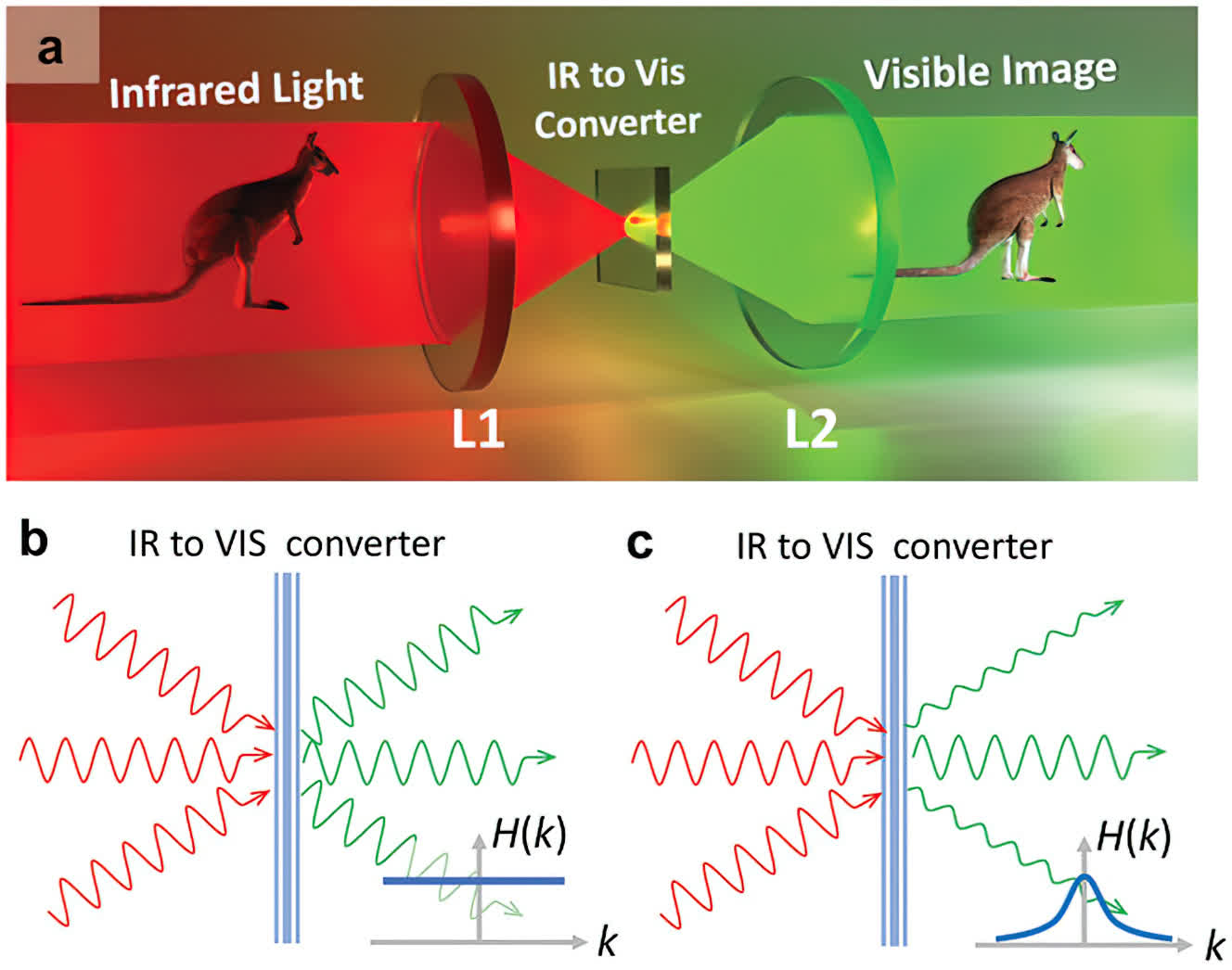
Researchers in Australia have now found that utilizing metasurface-based up-conversion expertise – an ultra-thin materials that may seize infrared and visual gentle on the similar time – on a regular basis eyewear may be augmented with night time imaginative and prescient. They revealed their findings final month in Superior Supplies.
The researchers, from TMOS, the ARC Centre of Excellence for Transformative Meta-Optical Techniques, created an infrared filter that’s thinner than a chunk of cling wrap, weighs lower than a gram, and will someday be positioned on an atypical pair of glasses.
A have a look at conventional night time imaginative and prescient expertise underscores the complexity of this filter’s process. Conventional night time imaginative and prescient requires infrared photons to go by a lens, encounter a photocathode that transforms these photons into electrons, which then go by a microchannel plate to extend the variety of electrons generated.
These electrons journey by a phosphor display to be reconverted again into photons, producing an intensified seen picture that may be seen by eye. These parts require cryogenic cooling to forestall thermal noise additionally from being intensified.
In distinction, with the metasurface-based upconversion expertise, photons go by a single resonant metasurface the place they’re combined with a pump beam. The resonant metasurface enhances the vitality of the photons, changing them into the seen gentle spectrum – no electron conversion wanted. It additionally works at room temperature, eliminating the necessity for cumbersome and heavy cooling techniques. Moreover, with up-conversion expertise, imaging techniques can seize each seen and non-visible gentle in a single picture.

The researchers’ authentic expertise featured a gallium arsenide metasurface. Their new metasurface is produced from lithium niobate, which is totally clear within the seen vary, making it much more environment friendly. Moreover, the photon beam is unfold over a wider floor space, limiting angular lack of information.
The researchers’ first demonstration of high-resolution up-conversion imaging transformed 1550 nm infrared gentle to seen 550 nm gentle in a non-local metasurface. They selected these wavelengths as a result of 1550 nm infrared gentle is usually utilized in telecommunications, and 550 nm is seen gentle to which human eyes are extremely delicate, in keeping with examine creator Rocio Camacho Morales. “Future analysis will embody increasing the vary of wavelengths the gadget is delicate to, aiming to acquire broadband IR imaging, in addition to exploring picture processing, together with edge detection.”
[ad_2]