[ad_1]
In relation to managing Waterfall tasks, probably the most necessary first steps is figuring out scope—what’s in and what’s out for the mission. This significant data is usually outlined in a mission scope assertion that names the mission’s main deliverables and exclusions. A well-crafted mission assertion could appear ample to ascertain the scope—and it may be. But I can attest to the unbelievable worth of going one step additional and creating a piece breakdown construction (WBS). It’s a step that’s too typically skipped.
The WBS is a visible mission administration software that does precisely what the identify implies: subdivides the product and corresponding tasks into distinct increments of labor. As a result of our brains prefer to work visually, the WBS turns into an efficient approach for the workforce to conceptualize its work.
Typically talking, scope is pushed by necessities elicited from the shopper or sponsor. A sponsor could method a mission supervisor with the preliminary parameters for a new product, corresponding to a line of laptops that the corporate will promote in North America. From there, the mission supervisor or enterprise analyst derives a collection of necessities, asking questions like, “What colours will the laptops be?” “What’s the arduous drive’s imply time between failures?” “What number of USB ports are wanted?” It’s necessary to keep in mind that, on this context, the scope contains something contributing to the mission’s final result. This implies not solely product scope (the options and capabilities of the laptop computer) but in addition mission scope (the work required to ship these outcomes). The mission scope might entail duties like lining up manufacturing for the laptop computer or allocating assets for mission administration.
Exclusions are essential to document within the scope assertion in order that later nobody asks one thing like, “Why aren’t we delivery to the UK?” As soon as accredited, this scope baseline helps forestall scope creep, which happens when somebody provides extra work with out contemplating its influence on schedule, prices, dangers, and assets. Any workforce member can test the scope assertion and see that each one the decision-makers signed off on which markets to prioritize, though in my expertise, many individuals by no means truly learn the scope assertion.
That’s the place the WBS is available in. When the workforce invests the time to develop a WBS collectively, it supplies a chance for everybody to visualise and interpret the whole thing of the scope—what’s in and what’s out—together with associated points corresponding to budgets and timelines. As such, I like to consider the WBS as a mission’s Rosetta stone.
What Is a Work Breakdown Construction?
The WBS was developed by the US Division of Protection within the Nineteen Fifties and continues to be generally utilized by authorities groups and contractors, provided that mission outcomes in these contexts are sometimes decided on the outset. The WBS will also be invaluable in different conditions the place Waterfall is required, which is extra widespread than many mission professionals could understand. Regardless of the ascendancy of Agile methodologies, which don’t embody the WBS as a part of the usual toolkit, 39% of knowledge expertise tasks nonetheless make use of Waterfall, in accordance with the Mission Administration Institute (PMI). In different industries, the chances are even greater.
The WBS breaks the mission scope into progressively smaller increments. This hierarchical rendering can seem in tabular or record codecs, however the most typical (and helpful) format resembles a household tree, with associated work grouped on totally different branches.
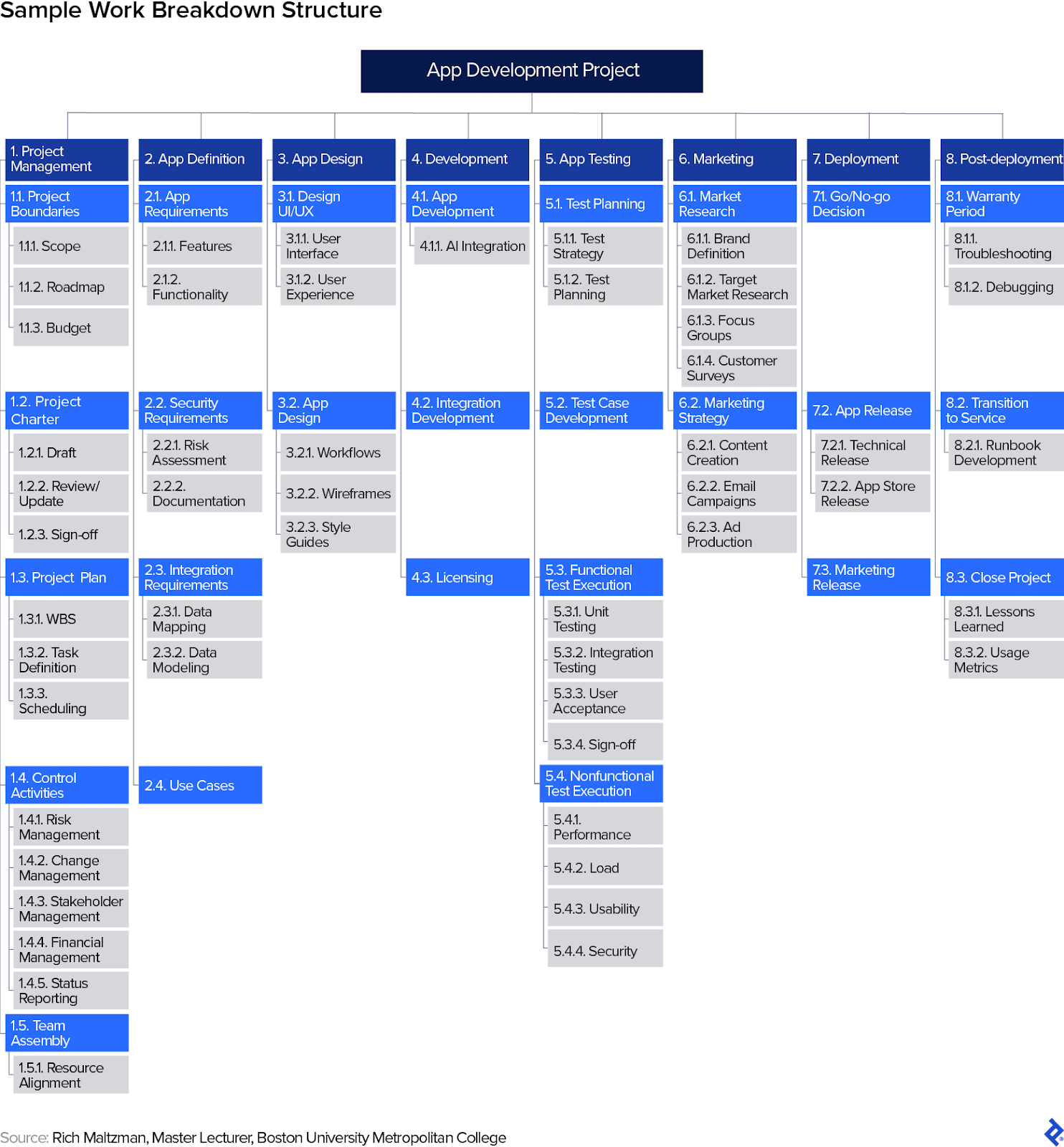
The primary degree of the WBS identifies the mission. The second degree divides the mission into phases, deliverables, or capabilities. The selection relies upon totally on workforce preferences, however I desire phases as a result of they extra readily align with Waterfall’s sequenced method. The next layers are then subdivided till reaching an increment referred to as a work bundle. Usually, work packages require not more than two weeks (80 hours) to finish, however that isn’t inviolate. In giant authorities or aerospace tasks, for instance, a piece bundle could take a number of hundred hours. I’ve not often seen a WBS drill down greater than 4 or 5 ranges. By then, the workforce ought to have ample data to know what work must be accomplished.
Typically a WBS will incorporate a specialised numbering scheme that echoes the hierarchical breakdown. Essentially the most primary type assigns a quantity to every merchandise within the second degree of the WBS (e.g., 1, 2, 3). Subsequent layers in every column are additional divided with decimal factors (e.g., 1.1, 1.2, 1.3; 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3). In my expertise, groups can obtain the planning advantages of the WBS with out the numbering scheme, however in authorities tasks, it’s usually a requirement.
It’s essential to notice that even when a workforce organizes a WBS in accordance with phases or capabilities within the second layer, the WBS continues to be a “what” doc, not a “who” or “when” doc. It ought to seize the whole thing of the work that should happen (typically referred to as the 100% rule) however not who does it or when. Nonetheless, as soon as the workforce has created a WBS to outline what work should happen, everybody can extra simply discuss these associated considerations.
So the place does the Rosetta stone a part of this are available in? The WBS is a visible reference that enables workforce members to align on a shared understanding of product and mission scope. It additionally helps the workforce start to make sense of different points, like prices, dangers, assets, and schedules. As PMI eloquently places it in its Apply Customary for Work Breakdown Buildings (a superb useful resource for anybody who needs to grasp the small print of this software): “The WBS creates a standard language amongst all mission stakeholders, together with mission administration and subject-matter features.” In my expertise, that is undoubtedly the case.
Create a Work Breakdown Construction
Ideally, WBS planning shouldn’t be a solitary exercise {that a} mission supervisor undertakes alone. It’s higher to develop the WBS with representatives of all of the groups concerned. This collaborative method is how the widespread language comes into being. Relying on the dimensions of the mission, one WBS could also be sufficient, though in some circumstances, every workforce could need to make its personal WBS.
As a marketing consultant, I’ve led mission kickoff occasions for quite a few organizations, together with world pharmaceutical firms, for which I co-facilitated in depth two-day working classes to plan new drug improvement tasks. The drug improvement course of can take 10 to fifteen years, however the scope is outlined at first. Stakeholders would attend from far-flung corners of the globe to fulfill and higher perceive the product they might ultimately be producing. When accomplished correctly, classes like this additionally function a superb team-building train. I ought to emphasize that the individual main this train needs to be an skilled facilitator.
Amongst different issues, my co-facilitator and I might train attendees the right way to craft and use a WBS. Representatives from every division—regulatory, advertising and marketing, manufacturing, gross sales, and so forth—would produce their very own WBS by making use of sticky notes to flip charts on the partitions of a giant convention room. (For distant conferences, Miro is a superb software for the same exercise.) Groups can develop the WBS by following a top-down or bottom-up method: Within the first state of affairs, a workforce arranges sticky notes that identify bigger work objects after which provides sticky notes representing subtasks. Within the second state of affairs, the subtasks are organized first. Staff preferences dictate which method works finest, however I’ve at all times discovered top-down simpler to examine.
Every workforce aimed to map out the whole thing of its scope. If that degree of element wasn’t attainable (as a result of a key consultant couldn’t attend or for some other motive), the workforce would nonetheless embody a planning bundle for these objects on the WBS and elaborate upon them later. The group brainstorming allowed the groups to visualise the complete contours of the proposed work. You possibly can think about the energetic debates that ensued. Individuals would say issues like, “Is that this actually what we’re doing?” or “That doesn’t belong right here; it belongs there.” On the finish of the two-day classes, every workforce had produced its personal WBS, and we had a visible image of the mission. The sponsor might look across the room and say, “Sure, there’s my product,” or “The place is the advertising and marketing requirement we mentioned?” By means of these discussions, the workforce understood the character of its work in better element.
Whereas the attendees had been mapping out their work, my colleague and I might enter the duties right into a scheduler like Microsoft Mission or Smartsheet. Then we targeted on linking the objects to provide an preliminary timeline for all the mission. The scope could require official approval and sign-off from the sponsor and different stakeholders, so the schedule created through the assembly is just a tough draft. Nonetheless, the schedule illustrates how a WBS has nearly instantaneous utility, permitting groups to start getting ready for the following mission steps. In the true world, groups typically skip WBS planning and bounce on to constructing a schedule, forcing them to consider “what” and “when” concurrently. In my expertise, the WBS supplies a invaluable alternative to element what goes into the scope first, earlier than figuring out when the work must happen.
It’s necessary to notice that specialised instruments might help mission managers develop a WBS. One is named WBS Schedule Professional, and it integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Mission. If a mission supervisor can not convey all the workforce collectively, both in individual or nearly, I nonetheless encourage mission managers to draft a WBS on their very own, maybe utilizing a specialised software. The mission supervisor can current this draft to the workforce at a gathering. The draft could get some issues improper, however imagine me, the workforce shall be blissful to right these points. That’s a great factor.
For the document, I additionally requested ChatGPT to generate a WBS for me, and it did so in a bulleted format. The final breakdown was surprisingly good. With cautious prompting, I think mission managers might flip to generative AI instruments for useful brainstorming help and even coax a picture generator corresponding to Dall-E 3 to render a graphical WBS. In fact, the outcomes would require double-checking for accuracy.
Different Outcomes of WBS Planning
Whereas the WBS could seem to be “merely” a scope software, it affords far more than that. Mission managers must concern themselves not solely with scope but in addition with prices, dangers, assets, stakeholders, and any variety of points. If a part of the scope is lacking, this implies there are:
- No assets related to it.
- No schedule allowed for it.
- No dangers recognized for it.
- No stakeholders specified.
- No assumptions made about it.
These points don’t go on the WBS, but when the workforce is already assembled in a big convention room for WBS planning—or collaborating nearly utilizing a software like Miro—it presents a superb alternative to start addressing them. In truth, I keep that there is no such thing as a higher time to do that, provided that the mission supervisor already has the appropriate folks in the appropriate place on the proper time. The workforce can have a look at the fleshed-out WBS and say, “How many individuals do I would like for this mission?” or “What are the dangers concerned?” And the sponsor could sigh and ask, “How a lot will all this value?”
Utilizing flip charts or on-line whiteboards, the workforce can begin to document dangers, assets, and motion objects in what we name parking tons. (The federal government formally defines the relationships between these associated considerations utilizing a doc referred to as a work breakdown construction dictionary. Nonetheless, I’ve by no means encountered a workforce that makes use of this dictionary in nongovernment contexts.)
Does the WBS Work in Agile?
An Agilist studying this may say, “All of this sounds nice, however can we use this?” Strictly talking, the reply is sure—PMI’s Apply Customary for Work Breakdown Buildings even features a part on utilizing the WBS in Agile. But I wouldn’t advocate it, provided that one of many primary variations between conventional mission administration and Agile is how scope is dealt with.
We usually use Waterfall after we—or the shopper or sponsor—have a really clear concept of what we wish as an finish outcome, final result, or product. Change is permissible however requires a considerably laborious change management course of. In Agile, the top outcome is just not as well-defined, permitting the sponsor or product proprietor the luxurious of fixing their thoughts because the mission evolves. This implies the scope might change from dash to dash—usually solely every week or two in length—so time spent creating the WBS would distract the workforce from the worth they need to give attention to delivering.
Higher Planning Means Higher Initiatives
The method of making a WBS could sound time-consuming, and it may be, particularly if a mission supervisor doesn’t have all of the stakeholders within the planning session or the necessities usually are not properly understood. With sufficient upfront preparation, nevertheless, making a WBS as a workforce is usually a little bit of a miracle. It brings everybody collectively, enforces planning, sparks dialog, and results in documented discussions about who, what, when, and the place. These outcomes will save time in the long term.
I’ve carried out a few dozen of the two-day planning workshops I described earlier, and we by no means failed to finish with a great general sense of the mission. If I’m managing a Waterfall mission, I’ll use the WBS at any time when attainable, even when I can’t pull the workforce collectively for 2 days. The WBS is key to planning, and, put merely, higher planning results in higher execution.
Need in-depth steerage on facilitating mission conferences? Jim’s ebook Nice Conferences Construct Nice Groups: A Information for Mission Leaders and Agilists affords sensible recommendation on bettering workforce cohesion and getting probably the most out of mission administration conferences and Agile occasions.
[ad_2]